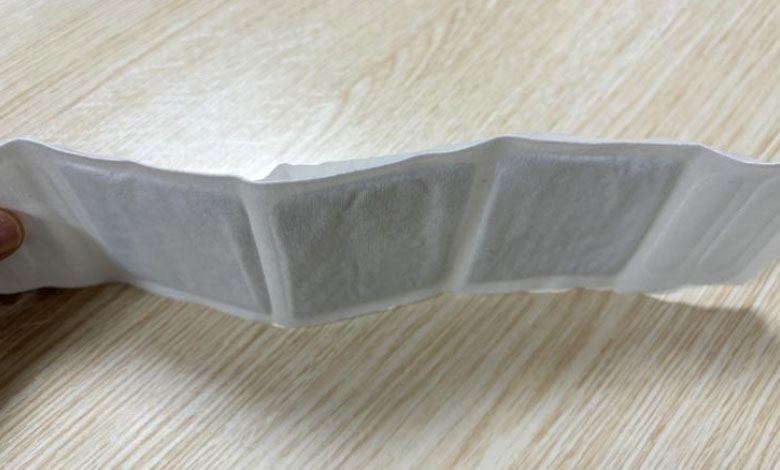
Heat patches are effective for pain relief and warmth, but users may notice they become hard and less flexible as they near the end of use. This is a normal result of the chemical reaction inside the patch.
Why Does the Patch Become Hard?
Depletion of Reactants: The heat is produced by the iron powder reacting with oxygen. Over time, as the iron is used up, the reaction slows down, and the patch becomes less flexible.
Moisture Loss: Heat patches rely on moisture to maintain the reaction. As moisture evaporates, the patch dries out and becomes rigid, especially with prolonged use.
End of Heat Production: Once most of the heat is released, the materials inside the patch solidify, making the patch dry and stiff.
Is It Safe to Use a Hard Heat Patch?
A hard patch usually means the chemical reaction is complete, and it’s no longer producing significant heat. While it’s not dangerous, the patch will no longer provide the same comfort or warmth. If it feels uncomfortable or damaged, discontinue use.
Conclusion
The hardening of a heat patch is a natural process that occurs as the chemical reaction slows down and moisture evaporates. While this doesn’t pose a safety risk, it signals that the patch is no longer actively producing heat. Always follow usage instructions to ensure the patch is effective during its use.
If you have concerns or discomfort, feel free to contact us.